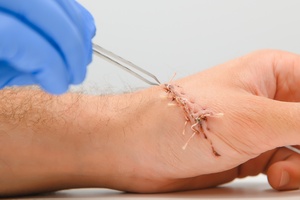
What Is Dry Socket?
Dry socket, also called alveolar osteitis, is a dental condition that can arise after the extraction of a tooth, particularly the wisdom teeth. DentalHealth.org explains that it occurs when the blood clot that forms in the socket where the tooth was removed either dislodges or dissolves prematurely, leaving the underlying bone and nerves exposed to air, food, and fluids. This exposure can lead to severe pain and delay the healing process. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and appearance of dry socket is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
Dry socket typically develops within a few days following a tooth extraction, according to the University of Columbia College of Dentistry. They explain that normally, a blood clot forms at the site of the extraction to protect the bone and nerve endings while the area heals. However, if the blood clot is lost or fails to form properly, the bone and nerves become exposed, leading to intense pain that can radiate to the ear, eye, temple, or neck on the same side of the face as the extraction. Additionally, the pain from a dry socket is often more severe than the discomfort experienced immediately after the extraction and may be accompanied by a foul taste or odor in the mouth, according to DentalHealth.org.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a dry socket, according to the Univerity of Columbia College of Dentistry, including smoking, using a straw, poor oral hygiene, and certain medical conditions. It is essential to follow post-operative care instructions provided by the dentist or oral surgeon to minimize the risk of this complication. If a dry socket does occur, prompt treatment is necessary to alleviate the pain and promote healing.
What Does Dry Socket Look Like?
A dry socket is characterized by the absence of the blood clot that should be present in the socket after tooth extraction. Instead of a dark blood clot, the socket may appear empty and have a whitish bone surface exposed, according to the National Institute of Health. The surrounding gum tissue may be inflamed and swollen, and there may be a noticeable gap where the tooth was removed. The visual signs of a dry socket, combined with severe pain, are key indicators that this condition has developed.
Dry Socket Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of a dry socket is crucial for timely intervention and effective pain management. This condition typically manifests within a few days following a tooth extraction and is marked by a distinct set of symptoms that differentiate it from the normal post-operative discomfort, according to the NIH.
They note that identifying these symptoms early can help in seeking prompt treatment and preventing further complications.
Symptoms of dry socket include:
-
Severe pain 1 to 3 days after the extraction
-
Pain that spreads from the socket to the ear, eye, or neck
-
Loss of the blood clot at the tooth removal site
-
Bad taste in your mouth
-
Bad breath
-
Slight fever
-
Visible bone in the socket
What Causes Dry Sockets? Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with dry sockets is essential for both prevention and effective management. Columbia Univerity College of Dentistry explains that dry sockets occur when the blood clot at the site of a tooth extraction is dislodged or fails to form properly, exposing the underlying bone and nerves. They go on to note that various behaviors and conditions can increase the likelihood of developing this painful complication. Identifying these risk factors can help patients take appropriate precautions to minimize their risk.
Some risk factors noted by Columbia Univerity College of Dentistry include:
-
Smoking cigarettes: The chemicals in cigarettes can interfere with the healing process and reduce blood flow to the gums, increasing the risk of a dry socket.
-
Suctioning, both when smoking and using a straw: The sucking motion can dislodge the blood clot from the extraction site, leading to a dry socket.
-
Insufficient oral hygiene: Poor oral hygiene can lead to infections and complications that may prevent proper clot formation and healing.
-
Taking oral contraceptives: Higher estrogen levels in oral contraceptives can affect the healing process and increase the risk of developing a dry socket.
-
Traumatic extraction: Difficult or complicated extractions can disturb the formation of the blood clot, making it more likely for a dry socket to occur.
-
Previous history of dry socket: Individuals who have experienced a dry socket in the past are at a higher risk of developing it again in future extractions.
Complications of Dry Socket
Dry socket is not only a source of severe pain but can also lead to several complications if not promptly and effectively treated, according to MouthHealthy.com. They note that the condition can significantly disrupt the normal healing process of the extraction site, causing prolonged discomfort and potential additional health issues.
One of the primary complications of a dry socket is delayed healing, according to DentalHealth.org. When the protective blood clot is lost or fails to form, the underlying bone and nerves are exposed to the oral environment, which can lead to inflammation and infection. This exposure can impede the normal healing process, causing the socket to remain open and painful for an extended period. As a result, the patient may experience persistent pain that lasts much longer than the typical post-extraction discomfort.
In addition to delayed healing, DentalHealth.org notes that the open socket can become a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to secondary infections. These infections can spread to the surrounding tissues and even into the bloodstream, posing a risk of systemic infection. Symptoms of a secondary infection may include increased swelling, redness, pus discharge, and fever. Therefore, it is crucial to seek prompt treatment for dry socket to mitigate these complications and ensure a smoother recovery process.
How to Prevent Dry Socket?
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding the painful and potentially complicated condition of dry socket, according to DentalHeath.org. They note that by taking specific precautions before and after a tooth extraction, patients can significantly reduce their risk of developing this issue. Understanding and implementing these preventive measures can help ensure a smoother and more comfortable recovery process — here are some tips for preventing dry socket, according to DentalHealth.org.
-
Avoid smoking: Refrain from smoking before and after the extraction, as the chemicals in cigarettes can impede healing and the suction motion can dislodge the blood clot.
-
Avoid oral contraceptives: If possible, discuss with your dentist the potential impact of oral contraceptives on your healing process, as higher estrogen levels can increase the risk of dry socket.
-
Avoid drinking through a straw: The suction created when using a straw can dislodge the blood clot, so it’s best to avoid this practice for several days following the extraction.
-
Check with your dentist if you should stop taking other medications that provide risk: Some medications may interfere with blood clot formation and healing, so consult your dentist about any drugs you are taking.
-
Follow your dentist’s instructions: Adhering to the post-operative care guidelines provided by your dentist or oral surgeon is crucial for preventing dry socket. These instructions are designed to promote proper healing and minimize complications.
-
Maintain good oral hygiene: Keeping your mouth clean can help prevent infections that might disrupt the healing process. Be gentle around the extraction site while brushing and rinsing.
Dry Socket Treatment and Self-Care
According to DentalHealth.org, treating a dry socket promptly is essential to alleviate pain and promote healing. Both professional dental care and self-care measures at home can help manage the symptoms and speed up recovery.
Understanding the available treatment options and self-care practices can provide relief and ensure a smoother healing process. Here are some treatment options for dry socket that are listed by DentalHealth.org:
-
Your dentist may clean the socket and fill it with a medicated dressing or paste: This helps protect the exposed bone and nerves while promoting healing and reducing pain.
-
Your dentist may provide antibiotics and prescribe pain medicine: Antibiotics can prevent or treat any infection, while prescription pain medication can help manage severe discomfort.
-
You may also buy over-the-counter medicine for pain: Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
-
At home, you may rinse with salt water to keep the socket clean: A gentle salt water rinse can help cleanse the area and prevent infection.
-
At home, you may apply ice on the jaw to numb the pain: Applying an ice pack to the affected area can reduce swelling and provide temporary pain relief.
-
Follow-up visits with your dentist: Regular check-ins with your dentist can ensure the socket is healing properly and allow for any necessary adjustments in treatment.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial in managing a dry socket effectively. While some discomfort is normal after a tooth extraction, certain symptoms indicate that you should consult your dentist promptly, according to MouthHealthy.org. Recognizing these warning signs can help prevent further complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
Here are recommendations from DentalHeath.org and MouthHealthy.org on when to seek medical health for dry socket symptoms:
-
If you are feeling the symptoms: If you experience symptoms of a dry socket, such as severe pain, exposed bone, or a foul taste in your mouth, it's important to contact your dentist as soon as possible.
-
If the pain is too intense: Extreme pain that radiates to other parts of your face or does not subside with over-the-counter pain relievers is a clear sign that you need professional intervention.
-
If the pain medicine does not work: If prescribed or over-the-counter pain medications are ineffective in managing your discomfort, you should consult your dentist for stronger medication or alternative treatments.
-
If you feel that your breath and mouth taste get worse: A worsening foul taste or bad breath can indicate an infection or complications that require immediate dental attention.
-
If you notice increased swelling or fever: These symptoms could be signs of an infection that needs prompt medical treatment.
FAQs
What is dry socket?
Dry socket is a painful dental condition that can occur after tooth extraction when the blood clot that protects the extraction site dissolves or dislodges, exposing the underlying bone and nerves.
What are the symptoms of dry socket?
Symptoms include severe pain, pain that spreads from the socket to the ear, eye, or neck, loss of the blood clot at the tooth removal site, bad taste in the mouth, bad breath, slight fever, and visible bone in the socket.
What are the risk factors for dry socket?
Risk factors include smoking, using a straw, poor oral hygiene, certain medical conditions, use of oral contraceptives, and traumatic tooth extraction.
How can I prevent dry socket?
You can prevent dry socket by avoiding smoking and drinking through a straw, maintaining good oral hygiene, following post-operative care instructions, and consulting with your dentist about the impact of any medications you are taking on your healing process.
How is dry socket treated?
Dry socket is treated with professional dental care and self-care measures, such as cleaning and filling the socket with a medicated dressing, antibiotics, pain medicine, over-the-counter pain relievers, salt water rinses, ice packs, and regular dentist check-ins.
Are there any home remedies for dry socket?
Yes, home remedies like rinsing with salt water and applying ice can help manage the pain.
When should I seek professional help for dry socket?
You should seek professional help if your symptoms persist or worsen, including severe pain, ineffective pain medication, worsening bad breath or taste, and increased swelling or fever.
Can dry socket delay the healing process after tooth extraction?
Yes, dry socket can delay the healing process after a tooth extraction.