
Feel better faster. Get care today.
From the clinic or your couch. Find high quality, same-day urgent care for you and your kids. Book an urgent care visit today.
A hemorrhage refers to the escape of blood from a damaged blood vessel, which can occur either internally or externally, according to MedlinePlus. This condition can arise from various causes, including trauma, medical conditions, or surgical complications. Hemorrhages can vary in severity, and their implications can be serious, necessitating a clear understanding of the underlying mechanisms and types of hemorrhages to ensure prompt and effective treatment.
In essence, a hemorrhage can be classified based on its location and the nature of the bleeding. External hemorrhages are visible and occur when blood escapes through the skin or mucous membranes, while internal hemorrhages happen within the body and may not be immediately apparent. The body’s ability to control bleeding depends on various factors, including the size and location of the blood vessel involved and the overall health of the individual. Recognizing the type of hemorrhage is crucial for determining the appropriate course of action and treatment.
Hemothorax: This type of hemorrhage occurs in the pleural cavity, where blood accumulates between the lungs and the chest wall, often due to trauma or injury. Symptoms may include chest pain, difficulty breathing, and decreased breath sounds on the affected side.
Intracranial Hemorrhage: This refers to bleeding within the skull, which can occur in various forms, such as subdural or epidural hematomas. It is often caused by head injuries and can lead to increased intracranial pressure, resulting in neurological symptoms like confusion, headache, or loss of consciousness.
Postpartum Hemorrhage: This condition involves excessive bleeding following childbirth and can occur immediately or up to 12 weeks after delivery. It is a significant cause of maternal morbidity and mortality, often due to uterine atony, retained placental tissue, or trauma during delivery.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: This type of hemorrhage occurs in the space between the brain and the tissues covering it, typically due to a ruptured aneurysm. Symptoms often include a sudden, severe headache, neck stiffness, and altered consciousness, making it a medical emergency.
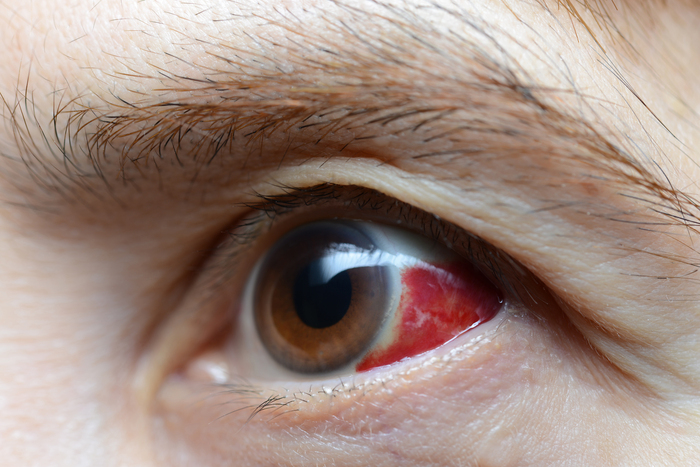
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage: This is a benign condition where blood accumulates between the conjunctiva and the sclera of the eye. It can occur due to minor trauma, straining, or certain medical conditions, usually presenting as a bright red patch on the white part of the eye without affecting vision.
Understanding the causes of hemorrhages is essential for prevention and timely intervention. Hemorrhages can result from a variety of factors, including lifestyle choices, medical conditions, and traumatic events, according to MedlinePlus. Identifying the underlying causes helps in managing risk factors and ensuring appropriate treatment when bleeding occurs.
Alcohol Use Disorder: Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage and impair the body’s ability to produce clotting factors, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Blood Clotting Disorders: Conditions such as antiphospholipid syndrome disrupt normal clotting processes, making individuals more susceptible to hemorrhage.
Hemorrhagic stroke: A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, leading to bleeding in or around the brain tissue. This type of stroke can cause significant damage due to increased pressure on brain cells and reduced blood flow, resulting in neurological deficits. Common symptoms include sudden severe headache, weakness, confusion, and loss of consciousness, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Blood Disorders: Inherited conditions like hemophilia and Von Willebrand disease affect the blood's ability to clot, leading to spontaneous bleeding or excessive bleeding from minor injuries.
Cancer: Certain cancers can compromise blood vessels or produce substances that interfere with normal clotting, resulting in increased bleeding risk.
Certain Medications: Anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, and some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can inhibit the blood’s ability to clot, heightening the risk of hemorrhage.
Certain Vascular Diseases: Conditions such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and aneurysms can weaken blood vessels, making them prone to rupture and bleeding.
Complications from Medical Procedures: Surgical interventions can sometimes lead to unexpected bleeding, either from the procedure itself or from complications during recovery.
Damage to Internal Organs: Conditions like stomach ulcers can erode blood vessels, causing internal bleeding that may not be immediately apparent.
Injuries: Traumatic injuries, including cuts, long bone fractures, or traumatic brain injuries, can result in significant external or internal bleeding.
Trauma: Severe trauma, such as gunshot or knife wounds, can cause extensive damage to blood vessels and tissues, leading to life-threatening hemorrhages. Small cuts and lacerations may cause bleeding, but usually not hemorrhages.
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers: Certain viral infections, such as Ebola or dengue fever, can cause widespread bleeding due to their effects on blood vessels and the immune system.
Recognizing the symptoms of hemorrhage is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms can vary significantly depending on the location and severity of the bleeding, as well as whether it is external or internal. Being aware of these signs can help individuals seek medical attention quickly, potentially preventing serious complications or worsening of the condition.
Dizziness and Nausea: These symptoms are usually caused by low blood pressure which can occur due to decreased blood volume and reduced oxygen delivery to the brain, often indicating significant blood loss.
Vomiting Blood: This alarming symptom may indicate internal bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, which requires immediate medical evaluation.
Changes in Mental State: Confusion, drowsiness, or altered consciousness can result from inadequate blood flow to the brain, signaling a critical situation.
Seizures: In severe cases of hemorrhage, particularly intracranial bleeding, seizures may occur due to increased pressure in the skull or disruption of normal brain function.
Swelling: Localized swelling may indicate bleeding in a specific area, such as a hematoma forming under the skin or in a muscle.
Pale, Gray, Clammy, or Sweaty Skin: These physical signs can reflect shock or significant blood loss, as the body diverts blood flow to vital organs.
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing may occur if there is internal bleeding affecting lung function or if blood loss leads to reduced oxygen levels in the body.
Extreme Thirst: A common response to significant blood loss, extreme thirst signals the body's need for fluids to help maintain blood volume and pressure.
The treatment of hemorrhage is highly dependent on its severity and location, as well as the underlying cause, according to AEDCPR.com. They explain that for minor or mild hemorrhages, initial care usually involves rest, hydration, and applying direct pressure to the affected area to help control bleeding. However, in cases of moderate to severe internal bleeding, more intensive medical intervention is required. This may include the administration of intravenous vitamin K to aid in clotting, as well as fresh frozen plasma, blood, and platelets to replenish lost components of the blood and stabilize the patient. Prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to minimize complications and improve outcomes in individuals experiencing hemorrhage.
Recognizing when to seek medical attention for hemorrhage is critical for ensuring safety and health, according to MedlinePlus. They explain that while minor cases of external bleeding can often be managed at home with basic first aid, internal bleeding poses a more significant risk and requires immediate medical intervention. Internal bleeding may not always present obvious symptoms, making it essential to be vigilant and aware of warning signs that indicate a serious condition.
If you experience any concerning symptoms or if bleeding persists despite applying pressure, it is crucial to seek medical help immediately. Ignoring the signs of a more severe hemorrhage can lead to life-threatening complications. Below are specific symptoms that warrant prompt medical attention:
Redness: Increased redness around a wound may indicate infection or ongoing bleeding.
Pain: Severe or worsening pain in the area of the bleeding could suggest complications that need evaluation.
The Wound Oozes Pus or Fluid: This can be a sign of infection, which requires medical treatment.
Swollen Glands: Swelling in nearby lymph nodes may indicate an infection or systemic response.
Fever: A fever accompanying bleeding can signal an infection or other serious condition.
Red Streaks Appear from the Wound in the Direction of the Heart: This could indicate the spread of infection and requires immediate attention.
Injury from a Bite, Whether Human or Animal: Bites can introduce bacteria and require evaluation for potential infections or rabies.
Tetanus Vaccination is Not Up to Date: If your tetanus vaccination is outdated (typically within the past five to ten years), medical evaluation is necessary to determine if a booster shot is needed.
Diagnosing hemorrhage involves a comprehensive assessment by healthcare providers, who rely on a combination of reported symptoms, observable signs, and physical examinations, according to the National Institute of Health (NIH). They explain that the process begins with a detailed medical history and a discussion of the patient's symptoms, which can provide critical clues about the nature and severity of the bleeding. Healthcare professionals will also observe any visible signs of hemorrhage, such as pallor, swelling, or unusual bruising, which can help guide their evaluation.
In addition to a thorough physical examination, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory tests may be employed to confirm the presence of hemorrhage, particularly in cases of suspected internal bleeding. This is particularly helpful for intracerebral hemorrhage, which is a hemorrhage that occurs around the brain tissue. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can provide detailed views of the body's internal structures, helping to identify the source and extent of the bleeding. Blood tests are also essential to assess the patient’s overall health, including hemoglobin levels, clotting function, and other relevant parameters. Together, these diagnostic approaches enable healthcare providers to accurately identify hemorrhage and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
If you or someone you know is experiencing bleeding that requires medical attention, don't hesitate to seek help. SolvHealth makes it easy to find an urgent care facility near you, ensuring you receive the prompt assessment and treatment you need. With a user-friendly platform, you can quickly locate nearby urgent care centers, check their availability, and even book an appointment online. Prioritize your health and get the care you deserve by using SolvHealth to connect with healthcare professionals who can address your concerns effectively.
A hemorrhage is a medical condition characterized by bleeding from a damaged blood vessel, which can occur either internally or externally.
Hemorrhages can result from a variety of factors, including lifestyle choices, medical conditions, traumatic events, and certain medications.
Symptoms of hemorrhage can include dizziness, nausea, vomiting blood, changes in mental state, seizures, swelling, pale or clammy skin, shortness of breath, and extreme thirst.
Treatment for hemorrhage depends on its severity and location, and can range from rest and hydration to more intensive medical intervention, such as the administration of intravenous vitamin K and fresh frozen plasma.
You should seek medical attention immediately if you experience any concerning symptoms or if bleeding persists despite applying pressure. Ignoring the signs of a severe hemorrhage can lead to life-threatening complications.
The symptoms of a hemorrhage can vary significantly depending on the location and severity of the bleeding. If you're experiencing severe bleeding, it's crucial to seek immediate medical help.
Yes, certain medications can potentially cause a hemorrhage. It's always important to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
Yes, trauma or injuries can damage blood vessels and lead to a hemorrhage. It's crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a hemorrhage after an injury or trauma.

From the clinic or your couch. Find high quality, same-day urgent care for you and your kids. Book an urgent care visit today.